



Share this on:
A conveyor belt is a looped belt that is driven by and wrapped around one or more pulleys. It is powered by an electric motor and supported by a metal plate bed or rollers upon which the conveyor belt rests. The pulley that powers a conveyor belt is referred to as the drive pulley and has an unpowered idler pulley.
Pulley drives at the discharge end of a conveyor belt are referred to as head drives, while ones located at the infeed end are known as tail drives. The preferred type of pulley drive is a head drive located at the discharge end and uses pull force to move a conveyor belt.
There is an endless number of types and uses for conveyors. All of the varieties serve the purpose of transporting materials and goods along a continuously moving path. Though motorized conveyor belts are the traditional form of a conveying system, some systems use rollers without a motor to move materials
The range and uses of conveyor belts cover several industrial settings and applications. The efficiency of conveyor belt systems assists in improving productivity, saves on labor costs, and decreases lead times. Conveyor belts move large quantities of goods quickly and reliably for transport, further assembly, or storage.
The principal reasons so many conveyor systems are in use are the savings in labor costs, efficient movement of goods, and protection of products and materials from damage. They provide the best possible service at the lowest possible cost.
• Roller Bed Conveyor Belt
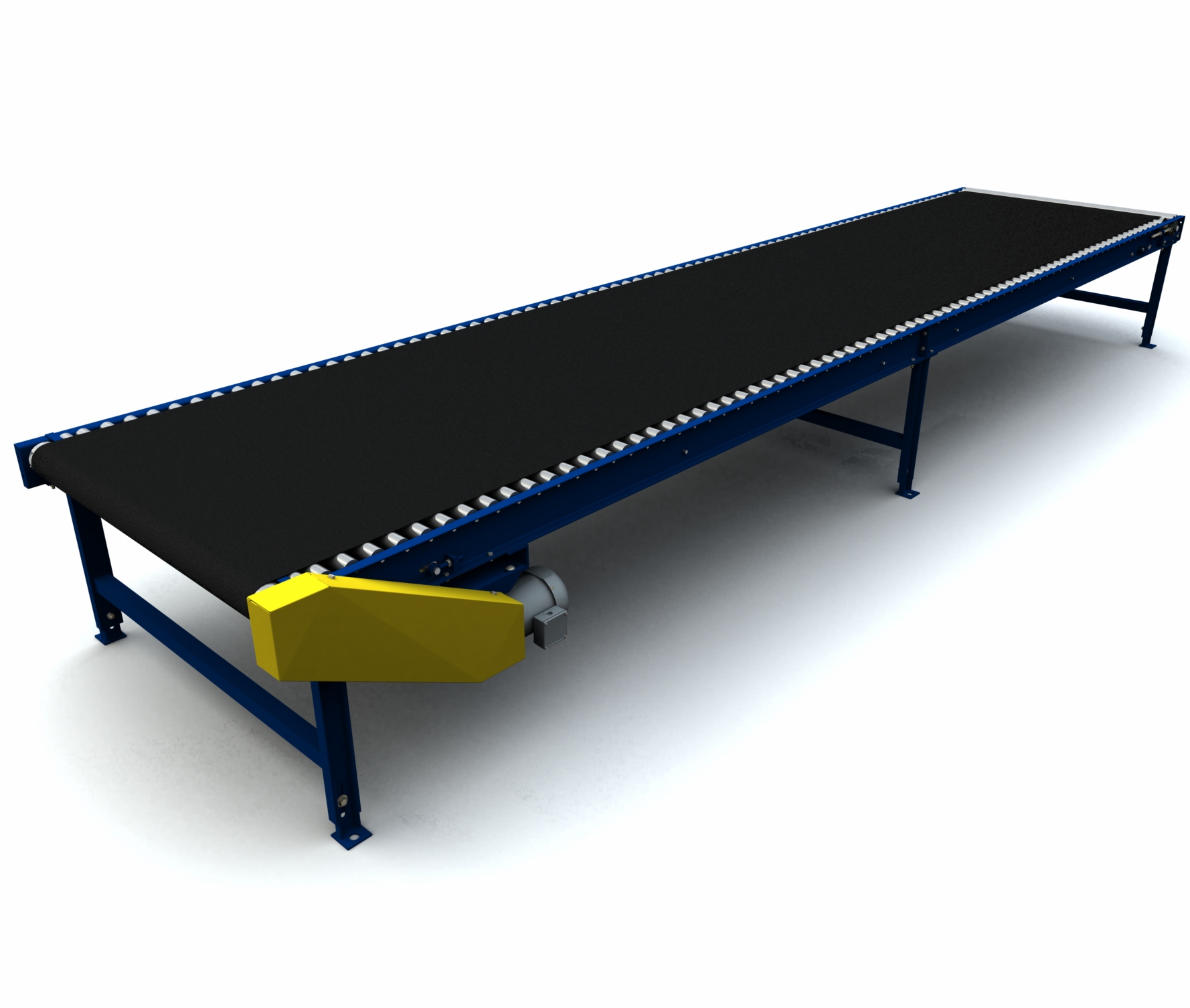
The surface of a roller bed conveyor belt consists of a set of rollers chosen to meet the needs of production requirements, such as speed, weight, and the type of products being moved. The length of a roller bed conveyor belt determines the number of rollers required.
Roller bed conveyors are ideal for conditions needing increased weight capacity. The roller bed design minimizes the amount of friction transferred to the belt, allowing for smooth product movement.
• Flat Belt Conveyor Belt
A flat belt conveyor belt uses a series of pulleys to move materials and supplies. Its belt is made of natural or synthetic materials; this makes it versatile and adaptable to varying conditions and applications. In some instances, a flat belt conveyor belt has a center drive and nose bars.
• Modular Conveyor Belt
A modular belt conveyor consists of interlocked pieces made of hard plastic with segments that can be easily removed and replaced. The design of modular belt conveyors makes them easier to clean, and the material is resistant to sharp and abrasive substances. Modular belt conveyors come in varying configurations and use a single belt to go around corners, in a straight line, and up and down declines.
• Cleated Conveyor Belt
Cleated belt conveyors have sections, pockets, or dividers that secure products when the belt declines or inclines. The cleats can be equally or unequally spaced and come in different styles and shapes, depending on the product and the design of the belt.
• Types of Cleats on Cleated Conveyor Belts
• Curved Conveyor Belt
The curves in conveyor belts are used to carry products around corners, make transfers, and make efficient use of floor space. Curved conveyor belts can make “U” turns to face the direction from which they came. They are made with flat belts and can turn at 45°, 90°, 135°, and 180° angles.
• Incline Conveyor Belt
There are several varieties of incline conveyor belts, with some having a rough, uneven surface while others have cleats to hold materials and prevent them from slipping or falling back. The underside of the belt has an even surface to allow the belt to glide smoothly along the bed. Modular conveyor belts can be used for this purpose. Cleats may be included for increased slippage prevention, depending on the moving material.
• Decline Conveyor Belt
The purpose of a decline conveyor belt is to move products or materials down or change its height. As with the incline version of conveyor belts, a decline conveyor belt has a rough surface or cleats to prevent materials from slipping or falling.
Decline conveyor belts are a continuous operating conveyor system with an articulated frame with a section that is pivoted or placed downward to accommodate the downward movement of products from an upper location.• Filter Conveyor Belt
Filter conveyor belts drain excess liquid from components or filter out toxins and contaminants. They are constructed with lateral grooves and holes in the center of the belt. Drainage holes are in a fabric-free zone down the center of the belt or sealed to prevent the liquid from soaking into the belt fabric.
Much like a sidewall conveyor belt, filter conveyor belts can have sidewalls to prevent liquids and fluids from spilling over the sides of the belt. They are made of heated polyester, polypropylene, polyolefin, or stainless steel mesh for dewatering applications.
• Timing Conveyor Belt
Timing conveyor belts are used for precision indexing and product placement. They are ideal for the positive placement of products regardless of the size of the product. Timing belt conveyors have a timing pulley and idler pulley with the timing belt looped around them. The teeth of the timing belt match the teeth of the pulleys with a support structure, conveyor frame, and support belt to hold the pulleys in place.
Precision conveying and accurate placement of products differentiate timing belt conveyors from conveyor belts in general. Timing belt conveyors can have different spacing between their teeth, which can be rounded or trapezoidal.
• Sandwich Conveyor Belt
A sandwich conveyor belt has two face-to-face belts, with one belt on top of the other to firmly hold materials. They have a rotating wheel for adjusting the pressure and gap between the belts. The materials to be moved are sandwiched between the two conveyor belts and hugged by the belts. The upper belt is not motorized and is moved by the force of the lower belt.
• Anti-Static Conveyor Belt
Electrostatic charge on a conveyor belt can be created by friction between the belt and the bed, the movement of the conveyed product, or ionization in the air. In most cases, the static current is of low intensity but can cause problems if materials stick to the belt. Though the charge is very low, it may cause sparks, leading to hazardous conditions.
Various devices can be installed on conveyor belt systems to dissipate and eliminate static charges. For example, anti-static belts might use carbon particles to make the belt anti-static or static-dissipative fabrics
Conveyor belts resemble a band or loop of rollers connected to rotors powered by a motor. The belts can be as narrow as one inch (25 mm) or as wide as five feet (1.5 m), with plastic modular belts as wide as ten feet (3 m). Conveyor belts are made of highly durable and sturdy materials, much like heavy-duty machinery.
The design of the belt provides structure and traction for the movement of goods and materials.
• Conveyor Belt Motors
The motor on a conveyor belt turns the pulleys that move the conveyor belt. A sufficient amount of friction between the belt and the pulleys will adhere the belt to the pulleys. The force of the conveyor motor rotates a drive pulley that moves the conveyor belt.
• Conveyor Belt Pulleys
Pulleys are positioned at either end of the conveyor belt and near the drive motor. The drive pulley drives the conveyor belt and has external bearings driven by a motor and reducer. Pulleys are crowned with lagging to reduce belt slippage.
Return, idler, or tail pulleys redirect the conveyor belt back to the drive pulley, have internal bearings, and are located at the end of the conveyor bed or at both ends of the conveyor with a center drive. The purpose of tail pulleys is to provide tension in the conveyor belt.
• Conveyor Belt Rollers
A conveyor belt is supported by a dead plate in the conveyor's frame. Rollers are used outside and underneath the conveyor to support the belt as it returns to the infeed. The center of the shaft of the rollers has a spring-retained axle used to install and remove it.
• Conveyor Belt
There are endless types, sizes, shapes, angles, and materials for conveyor belts. In a conveying system, the design and type of conveyor belt determine how it functions, and it is fabricated to carry materials and products from one location to another.
Regardless of the material used to produce a conveyor belt, all types are designed to move products, materials, supplies, and components efficiently and smoothly from one point to another. The type of product determines the type of conveyor belt and is the guiding aspect of conveyor belt selection.
Though there is a long list of materials used to make conveyor belts, all varieties fall into five categories: metal, plastic, rubber, fabric, and leather. There are subgroups and variations within each category.
• Plastic Modular Conveyor Belts
Plastic conveyor belts are lightweight and temperature-resistant belts made of thermoplastics such as polyurethane, polyester, polyvinyl chloride, silicone, and polyethylene. To allow for bending, curving, and incline or decline motion, plastic conveyor belts have interlocking segments that give them the flexibility to move in any direction. Interlocked plastic conveyor belts are an alternative to metal and fabric belts.
• Metal Conveyor Belts
Woven metal or plate conveyor belts are extremely strong, durable, rigid, and flat. Solid metal conveyor belts maintain their shape during their lifetime, while woven and linked conveyor belts will stretch and deform over time. Metal conveyor belts run in straight lines without curves, turns, or variations in their path. They are made from stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel and have exceptional longevity.
• Rubber Conveyor Belts
Rubber has been a conveyor belt material for many years and is one of the more durable choices due to its abrasion resistance. The types of rubber used for conveyor belts include neoprene, nitrile, and styrene butadiene, all of which are reinforced with cloth fabric.
The durability of rubber makes it ideal for harsh conditions where abrasion resistance and impact absorption are necessary. The cloth reinforcement prevents the rubber from stretching and deforming.
• Fabric Conveyor Belts
Fabric conveyor belts are a cost-effective choice for short conveying systems with lower capacity. The belt is made of several layers of synthetic fabrics that are specially treated to prevent elongation and have lengthwise polyester threads with crosswise polyamide threads. The combination of the two thread patterns provides an exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, flexibility, and resistance to impact and chemicals.
The top covers for conveyor belts are made of polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and silicone. In addition, rubber cover grades are added to fabric conveyor belts to make the belts resistant to fire, heat, and wear.
The types of fabric conveyor belts are:
• Leather Conveyor Belts
Leather conveyor belts were the earliest form of conveyor belts and are still used today. They are known for their durability, shock resistance, and good gripping. For modern conveyor belts, leather is used for custom and hybrid conveying systems. As with all conveyor belts, leather belts come in various widths and thicknesses. They can be reinforced with various forms of material and coated to enhance their performance. Leather conveyor belts can perform all of the traditional tasks of a conveyor belt, including incline and decline product movement.
•Uses for Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts can be found in any industry that requires the movement of materials or supplies from one position in the facility to another. Conveying systems have become an essential part of all industrial operations regardless of their size. Their quick and efficient movement of products makes them an ideal solution for improving supply chain performance. Larger, more complex facilities use automated systems for efficiency, time saving, and productivity.
The uses for conveyor belts range from small conveyors used to move jewelry and precious stones to outdoor conveyors configured to move rocks, coal, and ore. It’s very likely that a belt conveying system will be implemented for the rapid and economical movement of materials.
The various uses of conveyor belts can be broken into general and bulk material handling, food processing, and manufacturing and assembly operations.
• Bulk Material Handling
Bulk conveyor belts are used to move a wide variety of products and raw materials, including sugar, oats, cereal, fruit, flour, screws, nut fasteners, and food nuts. They quickly and efficiently load and unload cement, sand, and gravel. In mining, coal, minerals, rocks, and stones are moved from open and closed pit mining operations. The varying lengths of conveyor belts make it possible to remove minerals and refuse.
• Ship Loading and Unloading
Mobility is a crucial factor regarding the loading and unloading of ships. In the loading process, a belt conveying system unloads trucks and moves materials into the hold of a ship. For unloading, the process is reversed, and materials are moved from the ship and conveyed to trucks. Due to the unique nature of shipping and the different types of ships, loading and unloading belt conveyors are able to adjust to the height of the ship by telescoping.
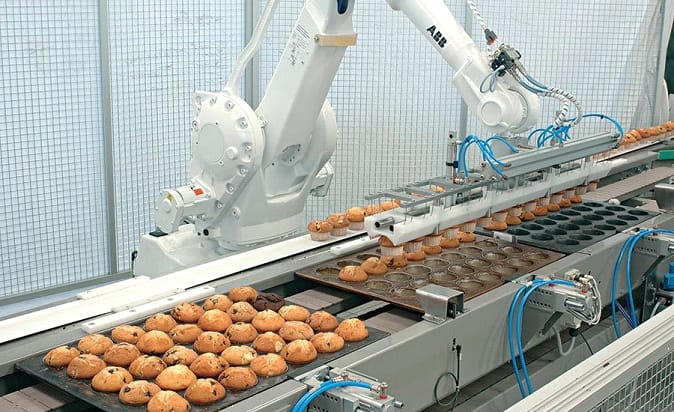
• Line Automated Assembly
Assembly operations have a series of conveyors that are custom-designed to fit the needs of the operation. As more and more assembly operations are using robotics and automated processes, belt conveying systems are being rapidly developed to meet the many computerized innovations and operational demands.
The varieties of belt conveyors used for automated assembly lines include chain, slider, hinged, plastic belt, and pallet. The increasing demand for rapid and efficient material movement has necessitated the creation of new and unique belt conveyor configurations.
• Luggage Transport
Belt conveyors are a necessary part of all airport operations in order to provide fast and efficient movement of packages, cargo, and luggage. For a belt conveying system to be successfully integrated into airport material handling, it must be able to meet the needs of all other handling and checking systems.
The specifications for airport belt conveyor systems include reliability, silent operation, appealing appearance, safety, and ease of maintenance. Every airport belt conveyor system is tailored to meet the specific requirements of the airport’s layout, including angles, flow rate, and one- or two-way operation.
• Parts Belt Conveyors
Parts belt conveyors can move and transport any type of part regardless of size or design, including hot, oily, and pressed parts from forging machines that need to be loaded in hoppers, storage units, and drums. Piano hinges are used due to their durability, strength, and rigidity. In addition, the weight and density of the part loads necessitate that the belt is made of shock- and impact-resistant materials, with sidewalls to prevent part spillage.
• Excavation Belt Conveyors
Excavation belt conveyors are designed to move earth and materials through small enclosed spaces such as windows, doors, and vents. Belt buckets are designed to handle loads of varying weights and have a high load capacity. Though excavation belt conveyors are capable of handling heavy loads, they can be easily maneuvered and positioned by two or three workers.